Follow_ETSAP – German Scientific Support for IEA Technology Collaboration Program on Energy Technology System Analysis
| Project coordination | Institute of Energy Economics and Rational Energy Use (IER), University of Stuttgart (PD Dr.-Ing. Markus Blesl) |
| Partners | Chair of Renewable and Sustainable Energy Systems (ENS), Technical University of Munich (Prof. Dr. Thomas Hamacher) Institute of Energy and Climate Research, Techno-economic Systems Analysis (IEK-3), Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH (Dr. –Ing. Heidi U. Heinrichs) |
| Funding | Federal Ministry of Economic Affairs and Climate Action |
| Duration | April 2023 until March 2026 |
| Contact | Anđelka Kerekeš, Thushara Addanki |
Overview of the research project Follow_ETSAP
The Energy Technology Systems Analysis Program (ETSAP) is one of the longest running Technology Collaboration Programs (TCP) of the International Energy Agency (IEA). The Follow-ETSAP project supports TCP ETSAP by contributing to the modeling of emission-free energy sources for the industry sector. A particular emphasis is placed on the competition among emission-free technologies against the background of material efficiency and the concept of circular economy. In addition to that, the role of new industries is analyzed. The findings are supplied to the ETSAP TIAM energy system model, which will be used to advance the understanding of the interrelationships between the aforementioned factors.
As part of this project, the aim of ENS is to determine the worldwide spatially resolved energy demand of aluminium, copper and chemical industrial sectors as part of a greenhouse gas-neutral energy system, depending on the identified energy demand drivers. For this purpose, data about global industrial sites are prepared and the existing models are further developed. Another goal is to determine the availability and costs of synfuels based on the exact locations of the renewable energy plants and industry as well as the identified transport infrastructure. The regional energy cost-related competition between hydrogen and synfuels will be examined together with the project partners. Furthermore, the effects of improved material intensity or material substitutions on material and energy demand will be examined for the case of automobile construction. The relationships and data developed will be prepared as an input for the ETSAP TIAM model.

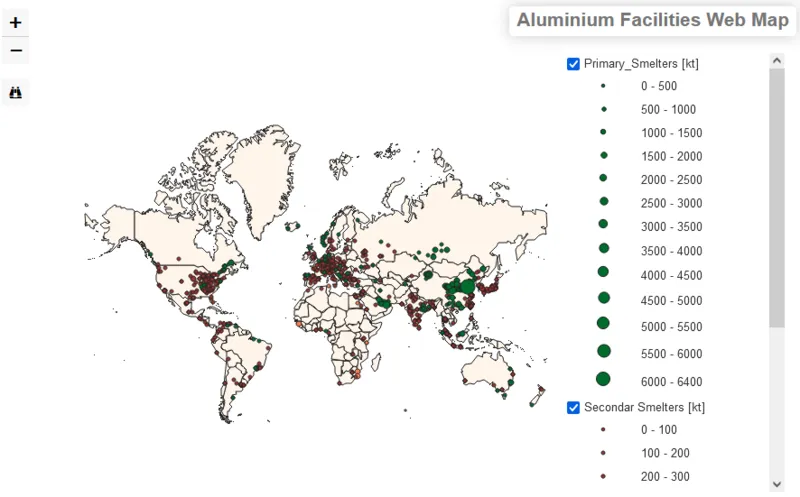
Partial result: interactive maps
The global industrial site data was determined and interactive maps were created. The figure shows an example of an excerpt from the map of the aluminum plants. The size of the location marker corresponds to the production intensity of the respective industrial site. The partial results are available in GitHub under the following link.