BoCTeR
The Biomass Combustion Test Rig „BoCTeR“ serves for the investigation of combustion processes using biomass as a fuel. The maximum thermal input is 200 kW. The test rig is a modification of the former test rig “OCTeR” which had been used for the oxyfuel combustion of coal.
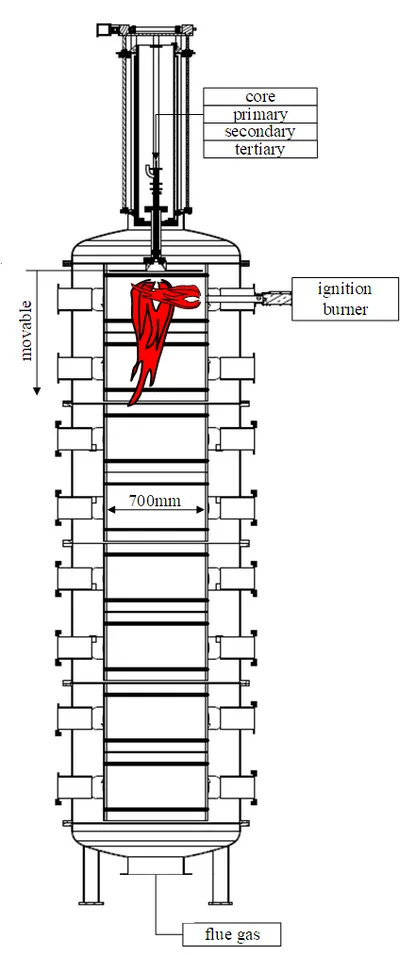
The combustion of the pulverized biomass fuel is realized through the so-called top-down method. The fuel is fed to the swirl burner which is located at the top of the combustion chamber.
The burner can be operated with pulverized biomass and/or natural gas as fuel. The dosing system of the pulverized biomass is realized with differential gravimetric dosing systems using twin screw feeders. The fuel is than transported by an air stream to the burner.
The fly ash in the flue gas is removed with a cyclone and a filter. Afterwards the flue gas is cooled down in order to condensate and collect the present water.
Cooling of the combustion chamber is realized by air cooled inner walls which are divided into eight different sections.
All measurements of the flame are performed using eight different port levels (four directions) with an vertical distance of 50 cm. At those ports flue gas analysis can be carried out. Therefor two gas analyzers are available which can measure CO, CO2, O2, NOx, HCl and the humidity in the flue gas. Besides flue gas analysis also temperature measurements of the flue gas using a suction pyrometer (type: IFRF) can be performed. Two cameras and an infrared camera enable (besides temperature measurement) online monitoring and evaluation of the flame stability.
Particle sampling is possible in any position of the combustion chamber. The use of an “Electronic low pressure impactors” (ELPI) enables the quantitative and qualitative analysis of fine particulates which were formed during combustion.
In order to increase the geometrical resolution of the vertical sample positions in the combustion chamber the burner is build in a support which can be moved vertically. This feature allows measurements using the same ports with a different relative distance to the burner mouth.